Haptic Touch
Haptic feedback and force measurement
A major disadvantage of the touch technologies used today, such as PCAP and infrared, is the lack of haptic feedback. Only it provides immediate feedback: The touchscreen vibrates and signals to the finger that the input has arrived. Especially in safety-relevant applications, there is a desire for more operating safety in combination with capacitive touchscreens.
Haptic feedback provides a new user experience by using the sense of touch to not only trigger an action, but also provide feedback to the operator. This enables "blind" operation without eye contact with the touchscreen. Measuring the actuation force allows further actions, such as palpating the controls or triggering the touchscreen only after a force has been applied. Different technologies are available, which can show their strengths depending on the application.
Haptics increase ergonomics and make operation possible without looking. A distinction is made between passive haptics through an appropriately designed surface and active haptics with feedback. As one of the leading suppliers of display and touch systems, we can offer you the right solution in the area of haptic touch.
Whitepaper: Touchscreens with Haptics
You can touch a mechanical switch. It acknowledges the switchover with a rich "clack". The operator is informed haptically and acoustically that the switching process was successful. This feedback is missing with a touchscreen: The actuation often takes place before a solid surface is touched and proceeds silently. The operator is left with the uncertainty: Have I pressed yet, and has the system perceived my touch?
Read detailed information on haptics in touchscreens - passive and active haptics, phases of a touch process, measurement of force, selective feedback, advantages and disadvantages of different actuators, and system integration.
Note: This white paper is in german.
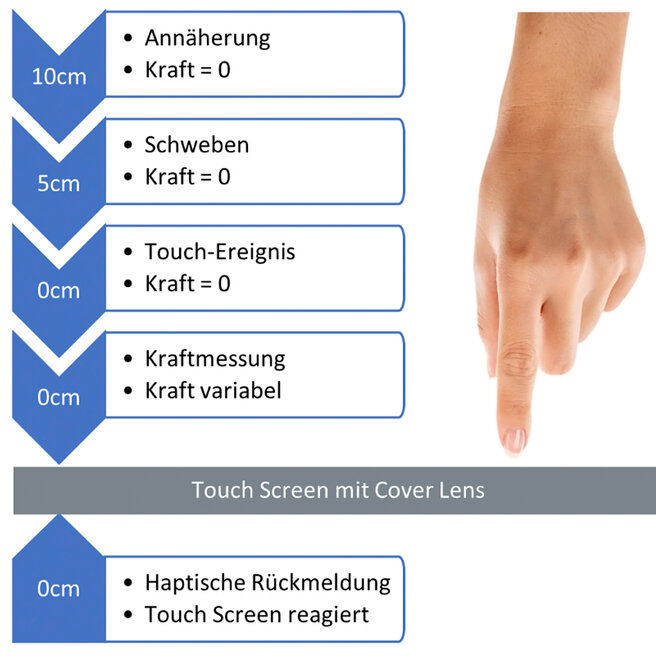
The figure shows the different phases of the detection of a touch event using the example of a PCAP touchscreen. When integrating a mechanical stimulation, care must be taken to ensure that the cover glass and the sensor are floating and sealed so that the vibrations can be transmitted to the finger and the system is protected from dust and moisture at the same time.
The actuation force can be measured to trigger specific actions. The host system can only pass the detected touch event to the system when the touch sensor is pressed firmly. Alternatively, a "second touch" function can be implemented to trigger a more advanced action.
For complete haptic integration, both methods can be combined.
Application examples for haptics
- Industrial Automation
- Handheld devices
- Automats
- Automotive industry (switch imitation)
- Addition of haptics to the AnySurface keyboard
- Medical technology
- Lifestyle and fashion
- Education
- Public displays
- Games
- VR and AR
- Accessibility
Consulting and contact
Your wishlist is empty