Energy saving displays
Different technologies in comparison
Especially for portable devices, independence from the mains and a compact design are important. The electronics should only consume a small amount of energy. Compared to the display logic, the backlight consumes a relatively high amount of power. So what should be done if it is to be energy-saving at the same time, but still easy to read even under bright ambient conditions such as outdoors?
Since the illumination of the display is one of the largest consumers, a technology that consumes as little energy as possible should be selected for the application. The illustration further below shows a comparison of the technologies presented here.
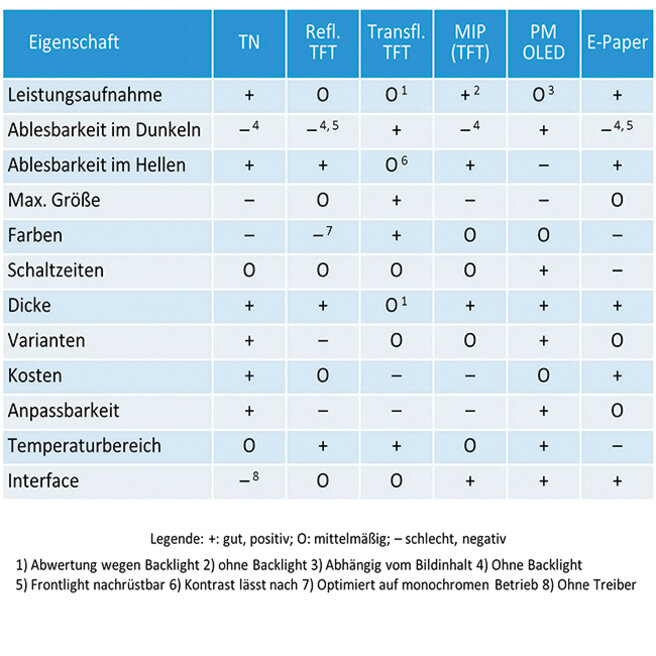
Reflective - transmissive - transflective
Reflective LCDs in TN and STN technology are used in simple applications such as calculators and energy meters. They use ambient light to provide sufficient contrast.
Transmissive displays have a built-in backlight. They work well in environments with moderate brightness. As ambient brightness increases, the intensity of the backlight must increase, which increases power consumption. In a typical TFT display (LG Display, 7" diagonal), the logic requires 0.9W, while the backlight at 450cd/m² requires 3W.
Transflective displays, on the other hand, use the incident light to increase contrast. Part of the inner structure reflects the light, while another part allows the light from the backlight to pass through. Transflective displays are available as LCD in TN and TFT. They are used where the display must be readable in both high and low ambient light.
Suitable technologies
TN
Advantages are the low unit prices and costs for a customized design compared to other technologies. Therefore, they are used in cost-sensitive applications such as utility meters. TN displays start with simple segmented displays such as the water purifier, move to seven-segment displays with custom icons, and finally to dot matrix displays.
Reflective TFT
Compared to TN, displays of higher resolution, better contrast and wider reading angle can be built. Power consumption is higher than TN, but still low. Like reflective TN displays, they rely on front illumination.
Transflective TFT
A transflective TFT can be used in all lighting situations. In the dark, the backlight shines through the TFT and color filter. In bright surroundings, the contrast is created by the light coming in from outside.
MIP
In MIP technology (Memory In Pixel), a memory cell is connected in parallel to the switching transistor for the pixel. As long as the supply voltage is applied, it retains the stored value. MIP is suitable for applications that have to manage with limited energy for a long time, such as wearables. MIP displays can be realized reflectively or transflectively.
Passive Matrix OLED
OLEDs are self-emitting. The color is determined by the materials used. OLEDs are particularly energy-saving when the image content is only thinly populated, i.e. when displaying text in "dark mode" with a dark image background and light font. The brightness of OLEDs is not very high, but the contrast is very high due to the dark background and thus the readability is very good. OLEDs do not have a polarizing filter, but there is a polarizing filter on the top that minimizes reflections.
E-Paper
E-paper technology uses bistable, polarized dyed beads that are embedded in a plastic carrier but are free to move. The carrier, in turn, is placed on a substrate whose voltage level influences the orientation of the beads. For the best contrast, the voltage level must be precisely maintained as a function of temperature. Once the elements have taken up their position, they retain it without energy until the next change.
Comparison of technologies
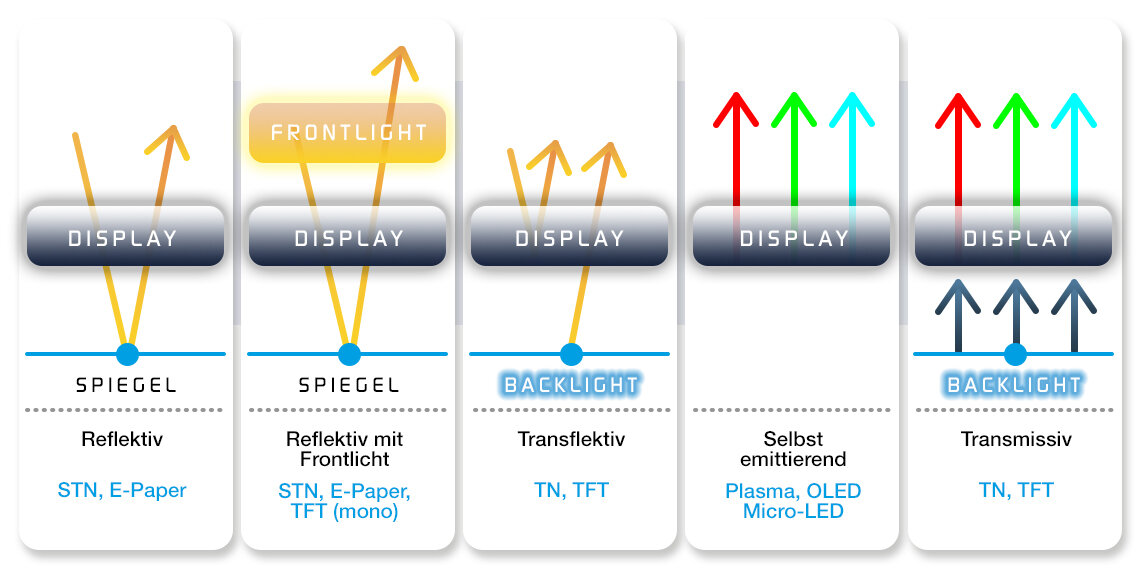
The table compares the different display technologies. Each technology has strengths and weaknesses, so it depends on the exact application which one is selected.
Explanation of the indices
- The transflective TFT consumes little power as long as the backlight is off.
- MIP also works (reflective) without backlight and has a very low power consumption, which is supported by the reduced frame rate.
- With passive matrix OLED, only the illuminated picture elements require power for operation (driver chip neglected).
- Non-self-illuminating technologies must be supported and illuminated in the dark with a backlight or frontlight.
- Frontlights are used especially for reflective TFTs and e-paper displays.
- Color saturation is reduced in transflective displays in reflective mode
- Purely reflective TFTs are optimized for monochrome displays (omission of the color filter)
Applications for energy saving displays
- Logistics: Checking in and out of goods, tracking, inventory.
- Mobile radio: Portable radios for police, fire department, rescue services
- Factory automation: Machine control, robots, PLC, process controllers
- Test and measurement: data acquisition, diagnostic devices, programming devices
- Medicine: diagnostic devices, monitoring display in pumps, patient monitor, defibrillator, thermometer
- Construction: construction machinery, surveying, agriculture, GPS
- Leisure: fitness equipment, sports watches, smart watch, golf cart, boat, e-bike
- Home automation: heating and air conditioning controllers, status indicators, solar inverters, food processors, energy meters (gas/water/electricity)
- Battery-powered devices: shaver, toothbrush, remote control
- Outdoor: ATM, point-of-sale terminal, e-charging station, gas pump
Consulting and contact
Your wishlist is empty